Vehicles
The game will deliver over 120 detailed rail, road, water and air vehicles from North America and Europe spanning a 150 year time period.
Vehicles feature a detail richness with e.g. emissive lights, modeled interiors and complex animations. They will catch rust and dirt over time to reflect the aging process. The paintwork is customizable and a custom company logo can be placed on the vehicles.
Select a vehicle below to get detailed information!
 4-4-0 The General |     | 4-4-0 The General This "American" type locomotive was very successful on many railroads in the USA and is well known from the Buster Keaton film "The General". Built: 1855 Top speed: 45 km/h Weight: 40 tons Power: 100 kW Traction: 30 kN |
 2-8-0 Baldwin Class 56 |     | 2-8-0 Baldwin Class 56 The "Consolidation" was a standard freight locomotive and could move trains twice as heavy at half the cost of its predecessors. Built: 1874 Top speed: 60 km/h Weight: 50 tons Power: 200 kW Traction: 60 kN |
 Alco PB |     | Alco PB The Alco PB is the cabless booster unit B which matched the PAs and increased the horsepower rating. Built: 1946 Top speed: 188 km/h Weight: 139 tons Power: 1680 kW Traction: 227 kN |
 Alco PA |     | Alco PA The Alco PA series has often been regarded as the most beautiful and aesthetically pleasing diesel locomotive ever built. Built: 1946 Top speed: 188 km/h Weight: 139 tons Power: 1680 kW Traction: 227 kN |
 EMD AEM-7 |     | EMD AEM-7 These locomotives used the latest in electric technology featuring thyristor motor control and traction motors that provided maximum power. Built: 1978 Top speed: 201 km/h Weight: 92 tons Power: 4320 kW Traction: 133 kN |
 GE C40-8W |     | GE C40-8W This 6-axle diesel-electric locomotive is distinguished from the Dash 8-40C by the addition of a "wide" or "safety" cab. Built: 1989 Top speed: 113 km/h Weight: 177 tons Power: 3000 kW Traction: 483 kN |
 D 1/3 Spanisch-Brötli-Bahn |     | D 1/3 Spanisch-Brötli-Bahn The legendary railway was known as the Spanisch-Brötli-Bahn, named after a Baden specialty. Built: 1847 Top speed: 30 km/h Weight: 30 tons Power: 66 kW Traction: 20 kN |
 A 3/5 |     | A 3/5 This 4-6-0 locomotive was the first really fast (100 km/h) locomotive of the Jura-Simplon and the Gotthard line. Built: 1907 Top speed: 100 km/h Weight: 114 tons Power: 1000 kW Traction: 120 kN |
 Class 75.4 Baden VI c |     | Class 75.4 Baden VI c This locomotive improved on the design of the Baden VI b and was equipped with a super heater, larger wheels and a longer wheelbase. Built: 1914 Top speed: 90 km/h Weight: 76 tons Power: 580 kW Traction: 85 kN |
 Ce 6/8 II Krokodil |     | Ce 6/8 II Krokodil Swiss locomotive known as the "Crocodile" (because of the long flat snouts and the green color), mainly for heavy freight Built: 1921 Top speed: 75 km/h Weight: 128 tons Power: 1650 kW Traction: 150 kN |
 Class VT 95 Railbus |     | Class VT 95 Railbus These vehicles were diesel-powered, twin-axle rail buses of light construction. They were employed in passenger train duties on less profitable branch lines. Built: 1950 Top speed: 90 km/h Weight: 13 tons Power: 96 kW Traction: 15 kN Capacity: 57 Passengers |
 Class 1042 |     | Class 1042 This powerful, four-axle locomotive was developed and built in Austria and used for universal purpose. Built: 1963 Top speed: 130 km/h Weight: 83.9 tons Power: 3260 kW Traction: 260 kN |
 RABDe 12/12 Mirage middle car |     | RABDe 12/12 Mirage middle car Three-part electric multiple unit for commuter traffic in Switzerland. With all-axle-drive and high power, it was optimized for high acceleration. Built: 1965 Top speed: 125 km/h Weight: 170 tons Power: 2444 kW Traction: 239 kN Capacity: 200 Passengers |
 Re 450 control car |     | Re 450 control car The double-deck BT-control car is part of the Re 450 commuter train composition. Built: 1989 Top speed: 130 km/h Weight: 52 tons Capacity: 90 Passengers |
 DUALSTOX middle car |     | DUALSTOX middle car This double deck EMU is equipped with a tilting-compensation which allows to pass bends faster. Built: 2014 Top speed: 200 km/h Weight: 400 tons Power: 3750 kW Capacity: 340 Passengers |
 2-8-2 Heavy Mikado |     | 2-8-2 Heavy Mikado "Mikados" were the most common freight locomotives until the end of steam. More than 9'500 were used in the USA. Built: 1918 Top speed: 80 km/h Weight: 219 tons Power: 1650 kW Traction: 240 kN |
 Milwaukee Road class EP-2 |     | Milwaukee Road class EP-2 The locomotives, commonly known as Bi-Polars, were one of the most interesting and complex designs ever developed. Built: 1919 Top speed: 113 km/h Weight: 240 tons Power: 3311 kW Traction: 516 kN |
 Class 246 Traxx P160 |     | Class 246 Traxx P160 Modern diesel-electric locomotive primarily used in passenger transport. Built: 2000 Top speed: 160 km/h Weight: 82 tons Power: 4200 kW |
 M-300 |     | M-300 These gas-powered, self-propelled passenger railcars were nicknamed "Skunks" because people said "You can smell 'em before you can see 'em.". Built: 1924 Top speed: 100 km/h Weight: 25 tons Power: 200 kW Capacity: 50 Passengers |
 EMD GP 9 |     | EMD GP 9 GM's Electro-Motive Division GP9 series found enormous success and became one of the most successful diesel locomotives ever built. Built: 1954 Top speed: 105 km/h Weight: 117 tons Power: 1305 kW Traction: 288 kN |
 PLM 220 C127 |     | PLM 220 C127 The very futuristic locking "Big C" is a pioneer among the aerodynamic locomotives. Built: 1890 Top speed: 60 km/h Power: 600 kW |
 LNER Class A3 |     | LNER Class A3 This Flying Scotsman set two world records for steam traction, becoming the first steam locomotive to be officially authenticated at reaching 100 miles per hour. Built: 1923 Top speed: 160 km/h Weight: 98 tons Traction: 130 kN |
 Class 218 |     | Class 218 A diesel-hydraulic locomotive from Germany, built for medium/heavy trains. Built: 1971 Top speed: 140 km/h Weight: 80 tons Power: 1839 kW Traction: 235 kN |
 EMD SD40-2 |     | EMD SD40-2 The SD40-2s have become icons. One can spot them in virtually any place on practically any given train. Built: 1982 Top speed: 105 km/h Weight: 167 tons Power: 3000 kW Traction: 410 kN |
 Ae 4/7 |     | Ae 4/7 A universal locomotive from Switzerland, very long-lasting thanks to the so-called Buchli drive. Built: 1927 Top speed: 100 km/h Weight: 121 tons Power: 2300 kW Traction: 196 kN |
 Class 103.1 |     | Class 103.1 This fast and heavy electric locomotive was, for a long period, the flagships of German rolling stock. Built: 1970 Top speed: 200 km/h Weight: 80 tons Power: 7440 kW Traction: 312 kN |
 Class E 94 |     | Class E 94 Electric heavy freight locomotive, known as the "German Crocodile". Built: 1940 Top speed: 90 km/h Weight: 119 tons Power: 3000 kW Traction: 363 kN |
 Class A4 |     | Class A4 A streamlined 4-6-2 steam locomotive designed by Nigel Gresley. The "4468 Mallard" still holds the world record as the fastest steam locomotive. Built: 1935 Top speed: 145 km/h Weight: 105 tons Power: 1986 kW Traction: 158 kN |
 CLe 2/4 Red Arrow |     | CLe 2/4 Red Arrow This express railcar, planned as a single unit vehicle, was very popular with the passengers. Built: 1935 Top speed: 125 km/h Weight: 13 tons Power: 315 kW Traction: 45 kN Capacity: 70 Passengers |
 HHP 8 |     | HHP 8 HHP-8 means "High Horse Power 8000". The twin-cab electric locomotive was manufactured for use by Westrail and the Maryland Area Regional Commuter system. Built: 2010 Top speed: 200 km/h Weight: 100 tons Power: 6000 kW Traction: 250 kN |
 4-4-2 Hiawatha |     | 4-4-2 Hiawatha These high-speed, streamlined "Atlantic" type locomotives were built by ALCO to haul the Milwaukee Road’s Hiawatha express passenger trains. Built: 1935 Top speed: 160 km/h Weight: 243 tons Power: 2940 kW Traction: 136 kN |
 Class 89 preussische T 3 |     | Class 89 preussische T 3 As a 0-6-0 tank locomotive, it was the first that was built to railway norms. Built: 1882 Top speed: 40 km/h Weight: 30 tons Power: 213 kW Traction: 40 kN |
 Class V 100 |     | Class V 100 This diesel-hydraulic locomotive was produced for non-electrified branch lines as a replacement for steam locomotives. Built: 1958 Top speed: 90 km/h Weight: 62 tons Power: 809 kW Traction: 177 kN |
 NoHAB AA16 |     | NoHAB AA16 This diesel-electric locomotive was an european licence-built variant of the american F-series from GM. Built: 1954 Top speed: 120 km/h Weight: 108 tons Power: 1450 kW Traction: 200 kN |
 Re 4/4 |     | Re 4/4 A light-weight locomotive for fast passenger-trains, the first in Switzerland equipped with bogies. Built: 1946 Top speed: 125 km/h Weight: 57 tons Power: 1850 kW Traction: 138 kN |
 Baldwin's Six-Wheels |     | Baldwin's Six-Wheels The flexible-beam truck or six-wheels-connected engine was invented by Matthias Baldwin in 1842. His aim was to use all the locomotive's weight for traction. Built: 1842 Top speed: 30 km/h Weight: 20 tons Power: 50 kW Traction: 20 kN |
 Ge E60 |     | Ge E60 An electric locomotive build for Amtrak. This version of the E60 is equipped with two cabs and two pantographs. Built: 1974 Top speed: 145 km/h Weight: 176 tons Power: 4000 kW Traction: 333 kN |
 Borsig |     | Borsig Borsig was a German company based in Berlin. For that time it was a very competitive model, but was still manufactured without a roofed cabine. Built: 1860 Top speed: 40 km/h Weight: 32 tons Power: 90 kW Traction: 25 kN |
 Class 53 Prussian G 3 |     | Class 53 Prussian G 3 The Class G 3 was a family of six-coupled, medium-powered, goods train, tank locomotives. Built: 1877 Top speed: 45 km/h Weight: 38 tons Power: 160 kW Traction: 35 kN |
 ALCO HH600 |     | ALCO HH600 The HH600 is an early switcher diesel-electric locomotive. HH standing for "High Hood", the name was only used unofficially, but came eventually to use in official context. Built: 1932 Top speed: 65 km/h Weight: 93 tons Power: 450 kW Traction: 125 kN |
 Class PRR GG1 |     | Class PRR GG1 Sporting a beautiful streamlined design the GG1 not only looked good but it also performed exemplary reaching speeds of over 100 mph and remained in service for many years. Built: 1934 Top speed: 160 km/h Weight: 215 tons Power: 3450 kW Traction: 291 kN |
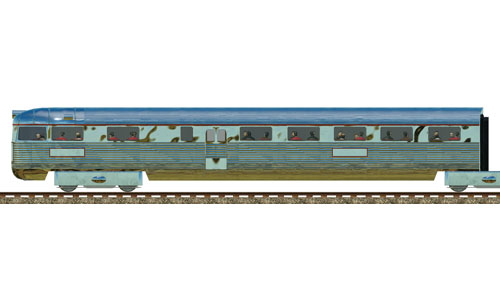 Pioneer Zephyr end car |     | Pioneer Zephyr end car The Zephyr is formed of cars permanently articulated together with Jacobs bogies and built by the Budd Company. The train featured extensive use of stainless steel. Built: 1934 Top speed: 177 km/h Capacity: 40 Passengers |
 Einheitswagen IV |     | Einheitswagen IV The four axle, twin bogie "Standard-Coach IV" was built on the experience with EW II and had an improved interior and, a first, air-conditioning. Built: 1981 Top speed: 200 km/h Weight: 42 tons Capacity: 86 Passengers |
 Class 185 |     | Class 185 One type of a modular product platform of electric and diesel-electric mainline locomotives from Bombardier Transportation, built in both freight and passenger variants. Built: 2000 Top speed: 160 km/h Power: 4200 kW |
 Speedance Express middle car |     | Speedance Express middle car Speedance Express trains are the fastest trainsets in the Americas; attaining 150 mph in revenue service on the NEC (North East Corridor). They use tilting technology to travel at higher speeds. Built: 2000 Top speed: 240 km/h Weight: 565 tons Power: 9200 kW Traction: 225 kN Capacity: 304 Passengers |
 Double-deck car |     | Double-deck car The double-deck B-car is part of the Re 450 commuter train composition. Built: 1989 Top speed: 130 km/h Weight: 52 tons Capacity: 98 Passengers |
 Re 450 commuter train |     | Re 450 commuter train A four axle electric locomotive, used for S-Bahn services. It even contains a luggage compartment which is rarely used. Built: 1989 Top speed: 130 km/h Weight: 74 tons Power: 3200 kW Traction: 240 kN |
 RABDe 12/12 Mirage end car |     | RABDe 12/12 Mirage end car Three-part electric multiple unit for commuter traffic in Switzerland. With all-axle-drive and high power, it was optimized for high acceleration. Built: 1965 Top speed: 125 km/h Weight: 170 tons Power: 2444 kW Traction: 239 kN Capacity: 200 Passengers |
 DUALSTOX commuter car |     | DUALSTOX commuter car This double deck EMU is equipped with a tilting-compensation which allows to pass bends faster. Built: 2014 Top speed: 200 km/h Weight: 400 tons Power: 3750 kW Capacity: 340 Passengers |
 Three-axle car |     | Three-axle car Three-axle coach with open platforms on both sides, used in Germany. Built: 1900 Top speed: 100 km/h Weight: 15 tons Capacity: 54 Passengers |
 BC4 |     | BC4 Four axle two bogie heavy coach for fast passenger service. Built: 1932 Top speed: 120 km/h Weight: 24 tons Capacity: 78 Passengers |
 Compartment car |     | Compartment car This compartment coach had two doors for each compartment, one on each side of the car. Easy for the passengers in and out, but impossible for a conductor to check the tickets while driving. Built: 1883 Top speed: 100 km/h Weight: 10 tons Capacity: 42 Passengers |
 Spanisch-Brötli-Bahn car |     | Spanisch-Brötli-Bahn car The legendary railway was known as the Spanisch-Brötli-Bahn, named after a Baden specialty. Built: 1847 Top speed: 50 km/h Weight: 5 tons Capacity: 22 Passengers |
 Donnerbüchse |     | Donnerbüchse Four-wheeled, standard, open coach made entirely of iron and steel. The lack of damping caused loud rumbling, hence the name "Thunderbox". Built: 1921 Top speed: 100 km/h Weight: 20 tons Capacity: 66 Passengers |
 Einheitswagen II |     | Einheitswagen II This four axle, twin bogie "Standard-Coach II" for passenger service was built in big series. Built: 1965 Top speed: 140 km/h Weight: 30 tons Capacity: 82 Passengers |
 TFV 2nd class coach |     | TFV 2nd class coach The famous French high speed train operated by the French national railway company. It is a permanently coupled electric multiple unit and was built for operation between Paris and the south-east of France. Built: 1981 Top speed: 300 km/h Capacity: 56 Passengers |
 Bavarian car |     | Bavarian car Two-axle coach with open platforms on both sides. Built: 1865 Top speed: 80 km/h Weight: 7 tons Capacity: 30 Passengers |
 Westrail Westfleet |     | Westrail Westfleet Westfleet is a fleet of single-level intercity railroad passenger cars built by the Budd Company for Westrail. The design is based on its earlier Metroliner electric multiple unit. Built: 1971 Top speed: 200 km/h Weight: 53 tons Capacity: 84 Passengers |
 Bombardier BiLevel |     | Bombardier BiLevel Bombardier BiLevel coaches are designed to carry up to 360 passengers for commuter railways. Easily identifiable, they are shaped like elongated octagons. Built: 1976 Top speed: 140 km/h Weight: 50 tons Capacity: 130 Passengers |
 All America Golden Sand |     | All America Golden Sand The former Southern Pacific coach "Golden Sand" was operated by All America. Built completely from aluminum, it featured advanced mechanical and operating systems. Built: 1950 Top speed: 140 km/h Weight: 35 tons Capacity: 76 Passengers |
 Passenger car |     | Passenger car An early passenger car with wooden structure, offering only basic amenities on board. Built: 1850 Top speed: 50 km/h Weight: 20 tons Capacity: 54 Passengers |
 Clerestory passenger car |     | Clerestory passenger car A passenger car with raised ceilings, called clerestory, to improve ventilation and increase comfort. Built: 1876 Top speed: 80 km/h Weight: 25 tons Capacity: 64 Passengers |
 Six-axle passenger car |     | Six-axle passenger car Heavy passenger car with more comfort to cover the long distances across the USA. Built: 1900 Top speed: 110 km/h Weight: 45 tons Capacity: 70 Passengers |
 Streamlined Coach New Mexico |     | Streamlined Coach New Mexico As a first effort to make coaches lighter, this type was built from aluminum with corrugated side walls. Built: 1937 Top speed: 120 km/h Weight: 30 tons Capacity: 72 Passengers |
 TFV 1st class coach |     | TFV 1st class coach The famous French high speed train operated by the French national railway company. It is a permanently coupled electric multiple unit and was built for operation between Paris and the south-east of France. Built: 1981 Top speed: 300 km/h Capacity: 35 Passengers |
 TFV Triebwagen |     | TFV Triebwagen The famous French high speed train operated by the French national railway company. It is a permanently coupled electric multiple unit and was built for operation between Paris and the south-east of France. Built: 1981 Top speed: 300 km/h Power: 6450 kW |
 Speedance Express railcar |     | Speedance Express railcar Speedance Express trains are the fastest trainsets in the Americas; attaining 150 mph in revenue service on the NEC (North East Corridor). They use tilting technology to travel at higher speeds. Built: 2000 Top speed: 240 km/h Weight: 565 tons Power: 9200 kW Traction: 225 kN Capacity: 304 Passengers |
 Pioneer Zephyr middle car |     | Pioneer Zephyr middle car The Zephyr is formed of cars permanently articulated together with Jacobs bogies and built by the Budd Company. The train featured extensive use of stainless steel. Built: 1934 Top speed: 177 km/h Capacity: 20 Passengers |
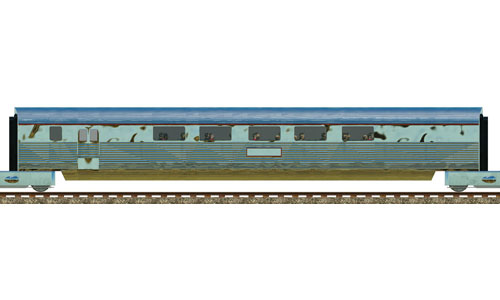 Pioneer Zephyr middle car |     | Pioneer Zephyr middle car The Zephyr is formed of cars permanently articulated together with Jacobs bogies and built by the Budd Company. The train featured extensive use of stainless steel. Built: 1934 Top speed: 177 km/h Capacity: 52 Passengers |
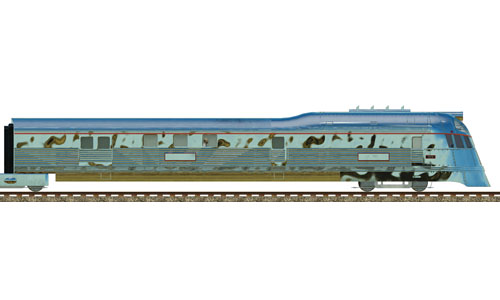 Pioneer Zephyr Railcar |     | Pioneer Zephyr Railcar The Zephyr is formed of cars permanently articulated together with Jacobs bogies and built by the Budd Company. The train featured extensive use of stainless steel. Built: 1934 Top speed: 177 km/h Weight: 80 tons Power: 448 kW |
 Heavyweight 28-1 Parlor |     | Heavyweight 28-1 Parlor The Heavyweight 28-1 Parlor is a luxury class wagon with 28 seats and a drawing room. Built: 1915 Top speed: 120 km/h Capacity: 28 Passengers |
 4-8-8-4 Big Boy |     | 4-8-8-4 Big Boy This articulated locomotive was a real monster and carried the latest in steam technology. They were used primarily to haul freight over the Wasatch mountains between Green River and Ogden. Built: 1941 Top speed: 130 km/h Weight: 567 tons Power: 4560 kW Traction: 602 kN |
 GE P42 DC |     | GE P42 DC The GE Genesis series is unique among recently manufactured North American passenger locomotives in that it uses a single, monocoque carbody design, thus making it lighter. Built: 2005 Top speed: 160 km/h Weight: 122 tons Power: 3170 kW Traction: 280 kN |
 4-12-2 Class 9000 |     | 4-12-2 Class 9000 These locomotives were fairly successful, but maintenance nightmares, because of their inside third cylinder. Built: 1926 Top speed: 97 km/h Weight: 355 tons Power: 3452 kW Traction: 430 kN |
 2-6-0 Mogul |     | 2-6-0 Mogul The 2-6-0 wheel arrangement was principally used on tender locomotives. This type of locomotive was widely built in the US from the early 1860s to the 1920s. Built: 1885 Top speed: 75 km/h Weight: 122 tons Power: 400 kW |
 4-4-2 Atlantic |     | 4-4-2 Atlantic This wheel arrangement is commonly known as the Atlantic type, although it is also sometimes called a Milwaukee. Built: 1906 Top speed: 100 km/h Weight: 130 tons Power: 700 kW |
 New Haven EP5 |     | New Haven EP5 The New Haven EP-5 was a double-ended mercury arc rectifier electric locomotive built by General Electric. It was built to haul passenger trains between New York City and New Haven. Built: 1955 Top speed: 140 km/h Weight: 159 tons Power: 3000 kW Traction: 151 kN |
 Boxcar |     | Boxcar An enclosed railroad car, generally used to carry all kind of freight. Built: 1850 Top speed: 80 km/h |
 Boxcar |     | Boxcar The boxcar, while not the simplest freight car design, is probably the most versatile, since it can carry most loads. Built: 1902 Top speed: 120 km/h |
 Boxcar |     | Boxcar A modern day boxcar, built in aluminum to save weight. Built: 1945 Top speed: 140 km/h |
 Stake car |     | Stake car A flatcar with stakes on both sides to transport lumber. Built: 1850 Top speed: 80 km/h Weight: 8 tons |
 Stake car |     | Stake car Centerbeam flatcar or lumber rack, designed for carrying lumber. Built: 1895 Top speed: 120 km/h Weight: 12 tons |
 Stake car |     | Stake car Modern day centerbeam flatcar for lumber. Built: 1952 Top speed: 140 km/h Weight: 15 tons |
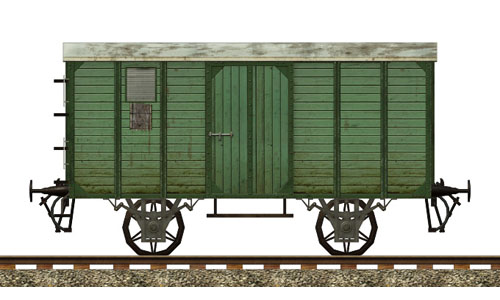 Goods wagon |     | Goods wagon Common used boxcar. Built: 1850 Top speed: 80 km/h |
 Goods wagon Hbi |     | Goods wagon Hbi Twin-axle boxcar with sliding doors, specially for sensitive goods on palettes. Built: 1970 Top speed: 200 km/h Weight: 14 tons |
 Verbandswagen |     | Verbandswagen Twin-axle boxcar built to standardize the fleet of freight cars. Built: 1910 Top speed: 120 km/h Weight: 11 tons |
 Tank wagon |     | Tank wagon Twin axle tank wagon. Built: 1860 Top speed: 80 km/h |
 Tank wagon |     | Tank wagon Twin axle tank wagon. Built: 1910 Top speed: 120 km/h |
 Tank wagon |     | Tank wagon Double bogie, four axle tank wagon. Built: 1950 Top speed: 140 km/h |
 Open wagon |     | Open wagon Twin axle freight wagon. Built: 1850 Top speed: 80 km/h |
 Open wagon |     | Open wagon Twin axle freight wagon. Built: 1910 Top speed: 120 km/h Weight: 10 tons |
 Open wagon |     | Open wagon Four axle freight wagon, particularly for mass transport. Built: 1975 Top speed: 140 km/h Weight: 15 tons |
 Stake car |     | Stake car Twin axle stake car. Built: 1850 Top speed: 80 km/h |
 Stake car |     | Stake car Twin axle stake car. Built: 1890 Top speed: 120 km/h |
 Stake car |     | Stake car Four-axle stake car. Built: 1950 Top speed: 140 km/h |
 Gondola |     | Gondola Twin bogie stake car. Built: 1850 Top speed: 80 km/h |
 Gondola |     | Gondola The gondola is the catchall of the railroad industry. Built: 1907 Top speed: 120 km/h |
 Gondola |     | Gondola As a modern gondola, these cars are used for carrying loose bulk materials. Built: 1955 Top speed: 140 km/h |
 Tank car |     | Tank car After oil was discovered in the 1860s, railroads were forced to develop this new type of car to transport liquids. Built: 1860 Top speed: 80 km/h |
 Tank car |     | Tank car A type of railroad car designed to transport liquid or gaseous commodities. Built: 1899 Top speed: 120 km/h |
 Tank car |     | Tank car A type of railroad car designed to transport liquid or gaseous commodities. Built: 1948 Top speed: 140 km/h |
 Metroliner |     | Metroliner The Metroliners, as extra-fare express trains between Washington, D.C., and New York City, were using self-powered electric multiple unit cars. Built: 1969 Top speed: 193 km/h Weight: 75 tons Power: 890 kW |
 Chevrolet C60 |     | Chevrolet C60 The C60 belongs to the Chevrolet/GMC B-Series and was built in many types and used as schoolbus, in mass transit and for other purposes. Built: 1974 Top speed: 80 km/h Weight: 6 tons Power: 160 kW Capacity: 35 Passengers |
 New Flyer Industries D40 |     | New Flyer Industries D40 The D40 was a transit bus built by New Flyer Industries. It used hollow tube side construction, clad with fiberglass panelling and wheel housings in stainless steel. Built: 1987 Top speed: 100 km/h Weight: 12 tons Power: 190 kW Capacity: 50 Passengers |
 Stage coach |     | Stage coach A common stage coach used for public transportation in the early years. Built: 1850 Top speed: 15 km/h Weight: 1 tons Power: 2 kW Capacity: 8 Passengers |
 Horse cart |     | Horse cart A two-horse vehicle with a simple twin axle carriage. Built: 1850 Top speed: 15 km/h Weight: 1 tons Power: 2 kW |
 Peterbilt 359 |     | Peterbilt 359 The durable Peterbilt 359 "Bull Nose" is considered a high-performance truck with low maintenance. Its powerful engine and many chrome parts made it a favorite of the North American truckers. Built: 1967 Top speed: 100 km/h Weight: 20 tons Power: 500 kW |
 MAN SL 192 |     | MAN SL 192 Standard public bus, built in big numbers. Built: 1972 Top speed: 90 km/h Weight: 16 tons Power: 141 kW Capacity: 64 Passengers |
 Volvo 5000 |     | Volvo 5000 This bus is a rear-engine, low-floor single-deck city bus with chassis built by Volvo and bodywork by Säffle. Built: 1993 Top speed: 100 km/h Weight: 10 tons Power: 120 kW Capacity: 72 Passengers |
 MAN 19.304 |     | MAN 19.304 A three axle lorry with a 230 hp V8 motor. It had, as a first, a foldaway cowling to ease maintenance. Built: 1970 Top speed: 100 km/h Weight: 6 tons Power: 250 kW |
 Mack AC |     | Mack AC The heavy duty AC, with its well known tapered hood, was the truck which started the bulldog theme. A 6.2l 4 cylinder engine and chain drive, it was strong, reliable, and worked well in rough terrain. Built: 1916 Top speed: 25 km/h Weight: 3 tons Power: 34 kW |
 Mercedes Benz O 6600 |     | Mercedes Benz O 6600 This city-omnibus, built by Mercedes-Benz, cost 52'785 DM at that time. Built: 1951 Top speed: 80 km/h Weight: 9 tons Power: 107 kW Capacity: 60 Passengers |
 L'Obéissante |     | L'Obéissante Built by the French Amédée Bollée, this steam omnibus was able to run bigger distances, e.g. from Le Mans to Paris. Built: 1873 Top speed: 25 km/h Weight: 1 tons Power: 4 kW Capacity: 12 Passengers |
 Berkhof Duvedec |     | Berkhof Duvedec Berkhof Duvedec received many good reviews of car owners for their consumer qualities. Built: 1989 Top speed: 90 km/h Weight: 15 tons Power: 180 kW Capacity: 100 Passengers |
 RTC Wrightbus |     | RTC Wrightbus The Wright StreetCar is an articulated bus developed by Wrightbus and Volvo. It consists of an adapted Volvo B7LA chassis, featuring a separate driver compartment at the front and is air-conditioned. Built: 2008 Top speed: 110 km/h Weight: 30 tons Power: 220 kW Capacity: 104 Passengers |
 Opel Blitz |     | Opel Blitz A very popular lorry from Opel, built in diverse variants. Built: 1930 Top speed: 95 km/h Weight: 3 tons Power: 74 kW |
 40 Tons Truck |     | 40 Tons Truck A six axle semi-trailer truck, equipped with a V8 turbo diesel engine of 456 kW power and 15,6 l dis-placement. Built: 1999 Top speed: 100 km/h Weight: 10 tons Power: 560 kW |
 DMG Cannstatt LKW |     | DMG Cannstatt LKW The first lorry of the world, with a Daimler motor, was delivered to Great Britain. Built: 1896 Top speed: 25 km/h Weight: 1 tons Power: 14 kW |
 Mack |     | Mack In 1900, the Mack brothers introduced their first successful vehicle. It operated in Brooklyns Prospect Park for eight years before being converted into a truck. The vehicle racked up a million miles of service. Built: 1900 Top speed: 24 km/h Weight: 4 tons Power: 24 kW Capacity: 20 Passengers |
 Studebaker US6 |     | Studebaker US6 The Studebaker US6 is a class of 2.5 ton trucks manufactured by the Studebaker Corporation during World War II, later used in civil service. Built: 1941 Top speed: 72 km/h Weight: 5 tons Power: 64 kW |
 Schneider PB2 |     | Schneider PB2 The Schneider PB2 was originally a French military transporter in World War I. Later it was exported and used as a bus in many American cities. Built: 1918 Top speed: 30 km/h Weight: 5 tons Power: 35 kW |
 GM Fishbowl |     | GM Fishbowl Commonly known by the nickname Fishbowl for its six-piece rounded windshield, more than 44'000 units of this iconic North American bus were produced. Built: 1960 Top speed: 80 km/h Weight: 8 tons Power: 160 kW Capacity: 55 Passengers |
 Landauer |     | Landauer The Landauer was basically a motor-driven carriage, built by the Benz company. As the first bus of the world, it was in use on the line Siegen-Nephten-Deuz. Built: 1895 Top speed: 20 km/h Weight: 2 tons Power: 10 kW Capacity: 8 Passengers |
 Twin Coach 44-S |     | Twin Coach 44-S Twin Coach was an American vehicle manufacturing company from 1927 to 1955, based in Kent, Ohio. Built: 1946 Top speed: 65 km/h Weight: 7 tons Power: 88 kW Capacity: 44 Passengers |
 Postbus ET 13 |     | Postbus ET 13 The ET 13 was a commonly used motor-driven bus, built in Austria. Built: 1900 Top speed: 24 km/h Weight: 4 tons Power: 20 kW Capacity: 20 Passengers |
 Daimler top-seater |     | Daimler top-seater An early top-seater bus, used by ABOAG, a public transportation company in Berlin, Germany. Built: 1924 Top speed: 25 km/h Weight: 5 tons Power: 35 kW Capacity: 30 Passengers |
 Ford Model 77 |     | Ford Model 77 An ubiquitous truck, built as a standard platform with a lot of different bodies, for example pickup, sedan, stake bed truck and panel delivery truck. Built: 1935 Top speed: 40 km/h Weight: 2 tons Power: 44 kW |
 Freightliner Cascadia |     | Freightliner Cascadia The Cascadia is a heavy duty semi-trailer truck and the flagship of Freightliner. It was available in fuel efficient and high performance models. Built: 2009 Top speed: 100 km/h Weight: 25 tons Power: 405 kW |
 Saurer Tüscher |     | Saurer Tüscher An urban public-transit bus, based on a Saurer carriage and a Tüscher car body. Built: 1940 Top speed: 55 km/h Weight: 8 tons Power: 80 kW Capacity: 52 Passengers |
 Steam Lorry |     | Steam Lorry Steam wagons were a widespread form of powered road traction for commercial haulage in the early part of the twentieth century. Built: 1890 Top speed: 25 km/h |
 Benz |     | Benz A typical early lorry by Mercedes-Benz still running on solid rubber tires. Built: 1910 Top speed: 50 km/h Weight: 2 tons Power: 35 kW |
 Horse cart |     | Horse cart A two-horse vehicle with a simple twin axle carriage. Built: 1850 Top speed: 15 km/h Weight: 1 tons Power: 2 kW |
 Horse cart |     | Horse cart A two-horse vehicle with a simple twin axle carriage. Built: 1850 Top speed: 15 km/h Weight: 1 tons Power: 2 kW |
 Horse cart |     | Horse cart A four-horse vehicle with a simple twin axle carriage. Built: 1870 Top speed: 20 km/h Weight: 1 tons Power: 2 kW |
 Stage coach |     | Stage coach A common stage coach used for public transportation in the early years. Built: 1875 Top speed: 15 km/h Weight: 1 tons Power: 2 kW Capacity: 8 Passengers |
 Stage coach |     | Stage coach A common stage coach used for public transportation in the early years. Built: 1850 Top speed: 15 km/h Weight: 1 tons Power: 2 kW Capacity: 4 Passengers |
 Studebaker US6 |   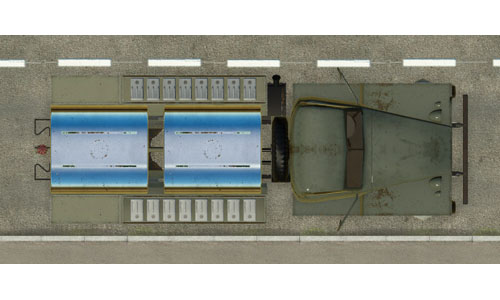  | Studebaker US6 The Studebaker US6 is a class of 2.5 ton trucks manufactured by the Studebaker Corporation during World War II, later used in civil service. Built: 1941 Top speed: 72 km/h Weight: 5 tons Power: 64 kW |
 Studebaker US6 |     | Studebaker US6 The Studebaker US6 is a class of 2.5 ton trucks manufactured by the Studebaker Corporation during World War II, later used in civil service. Built: 1941 Top speed: 72 km/h Weight: 5 tons Power: 64 kW |
 Halle tram |     | Halle tram Twin axle electrical tram with open platforms on both ends, used by the "Allgemeine Elektricitäts-Gesellschaft". Built: 1887 Top speed: 25 km/h Weight: 12 tons Power: 30 kW Capacity: 18 Passengers |
 Ce 2/2 SchSt |   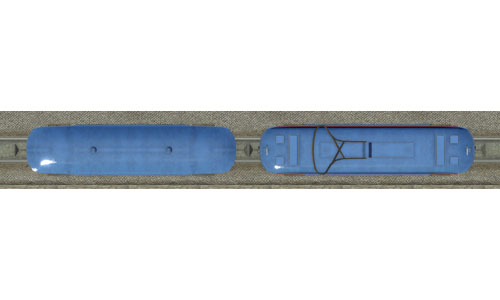  | Ce 2/2 SchSt Twin axle electrical tram from the home town of Transport Fever, Schaffhausen. Built: 1901 Top speed: 40 km/h Weight: 20 tons Power: 60 kW Capacity: 40 Passengers |
 Be 5/6 Cobra |     | Be 5/6 Cobra The first completely low floor tram runs through the city like a snake with its four joints. This gave it the nickname "Cobra". Built: 2001 Top speed: 70 km/h Weight: 39 tons Power: 625 kW Capacity: 96 Passengers |
 Gothaer Type T1 |     | Gothaer Type T1 From this type T1, built by Gothaer Waggonbau/Bothman, an example is still running as a museum train. Built: 1928 Top speed: 60 km/h Weight: 26 tons Power: 120 kW Capacity: 48 Passengers |
 Steam tram |     | Steam tram Twin axle locomotive of the steam tram as used e.g. in vienna as "Dampftramway". Built: 1877 Top speed: 20 km/h Weight: 8 tons Power: 15 kW Capacity: 20 Passengers |
 Be 4/6 Mirage |     | Be 4/6 Mirage The big cost-overrun during the acquisition of this tram led to its nickname "Mirage", the fighter plane which also cost much more than foreseen. Built: 1966 Top speed: 60 km/h Weight: 26 tons Power: 300 kW Capacity: 45 Passengers |
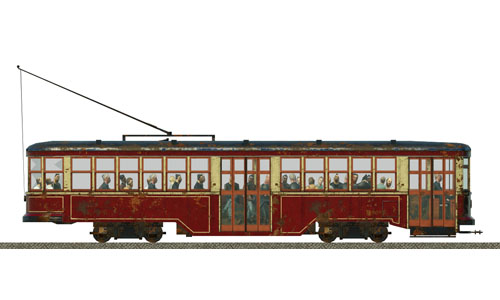 Peter Witt Streetcar |     | Peter Witt Streetcar Designed by Cleveland Railway commissioner Peter Witt, this streetcar was used in many North American cities, most notably in Toronto and Cleveland. Typical is the use of the center door as an exit only. Built: 1915 Top speed: 35 km/h Weight: 4 tons Power: 40 kW Capacity: 44 Passengers |
 San Diego |     | San Diego The Citizens Traction Company converted old cable cars to electrics. Later, the San Diego Electric Railway took over the Citizens company and converted the line to standard gauge. Built: 1889 Top speed: 20 km/h Weight: 2 tons Power: 4 kW Capacity: 28 Passengers |
 Toronto CLRV |     | Toronto CLRV The CLRV (Canadian Light Rail Vehicle) was the successful attempt to replace the aging PCCs by a modern, standardized streetcar. Built: 1979 Top speed: 60 km/h Weight: 23 tons Power: 272 kW Capacity: 64 Passengers |
 PCC 1643 Pittsburgh |     | PCC 1643 Pittsburgh The Presidents’ Conference Committee streetcar design proved very successful. As an example, Pittsburgh Railways operated 666 PCCs on 68 routes. Built: 1945 Top speed: 45 km/h Weight: 8 tons Power: 100 kW Capacity: 50 Passengers |
 Toronto PCC A-7 |   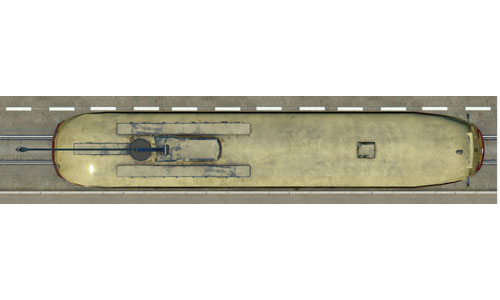  | Toronto PCC A-7 The PCC A-7 ran on Toronto's busiest line, the ten-mile-long crosstown Bloor line, restrained by 56 traffic signals on a roundtrip. Built: 1949 Top speed: 50 km/h Weight: 17 tons Power: 144 kW Capacity: 56 Passengers |
 Skoda 10 T |     | Skoda 10 T The Skoda 10 T is a three-carbody-section low-floor bi-directional tram, developed by Skoda Transportation. Built: 2000 Top speed: 70 km/h Weight: 29 tons Power: 360 kW Capacity: 170 Passengers |
 Horse trolley car |     | Horse trolley car The first trams in history were horse driven on rails. Due to the rail only one horse was enough. Built: 1870 Top speed: 20 km/h Power: 2 kW Capacity: 20 Passengers |
 Horse tram |     | Horse tram The first trams in history were horse driven on rails. Due to the rail only one horse was enough. Built: 1850 Top speed: 15 km/h Weight: 1 tons Power: 2 kW Capacity: 20 Passengers |
 Horse tram |     | Horse tram The first trams in history were horse driven on rails. Due to the rail only one horse was enough. Built: 1850 Top speed: 15 km/h Weight: 1 tons Power: 2 kW Capacity: 20 Passengers |
 Junkers F 13 |     | Junkers F 13 The world's first all-metal transport aircraft. An enclosed and heated cabin allowed room for four passengers. Built: 1920 Top speed: 160 km/h Capacity: 4 Passengers, 2 Crew |
 Douglas DC-3 |     | Douglas DC-3 The speed and range of this twin engine metal monoplane revolutionized air transport in the 1930s and 40s. Built: 1936 Top speed: 280 km/h Capacity: 32 Passengers, 2 Crew |
 de Havilland DH-106 Comet 4B |   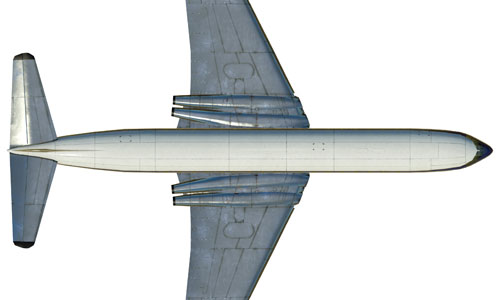  | de Havilland DH-106 Comet 4B Short range airplane produced in the late 1950s. A further development of the world´s first production jetliner, the Comet 1. Built: 1959 Top speed: 805 km/h Capacity: 85 Passengers, 4 Crew |
 Airbus A320 |     | Airbus A320 The A320 is a very poplar twin-engine jet airliner. Several thousand models have been produced with most of them still in operation. Built: 1988 Top speed: 890 km/h Capacity: 160 Passengers, 2 Crew |
 Boeing 757-200 |     | Boeing 757-200 This twinjet for short and medium routes uses turbofan engines allowing takeoffs from relatively short runways and higher altitudes. Built: 1983 Top speed: 850 km/h Capacity: 239 Passengers, 2 Crew |
 Douglas DC-4 |     | Douglas DC-4 The DC-4 is a popular airplane built during and after 2nd world war. A lot of them where converted for civil use, of which some remain in service until today. Built: 1942 Top speed: 365 km/h Capacity: 60 Passengers, 2 Crew |
 Dornier Do-B Merkur |     | Dornier Do-B Merkur Shortly after being build, a Merkur set seven records within a few days. Among these records: Traveling a distance over 7000km without an incident. Built: 1925 Top speed: 175 km/h Capacity: 6 Passengers, 2 Crew |
 Boeing 737 |     | Boeing 737 The Boeing 737 is short- to medium range twinjet narrow-body airliner. A lot of different variants have been produced since 1967. Built: 1967 Top speed: 907 km/h Capacity: 100 Passengers, 2 Crew |
 Concorde |   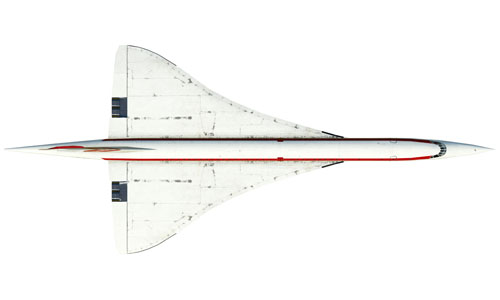  | Concorde The Concorde is a commercial British-French supersonic passenger airplane. The top speed is Mach 2.04, more than twice the speed of sound. Built: 1976 Top speed: 2179 km/h Capacity: 95 Passengers, 3 Crew |
 Lockheed Super Constellation L-1049 |     | Lockheed Super Constellation L-1049 The L-1049 was built during the 1950s in many different variations for civil as well as military use. Built: 1951 Top speed: 531 km/h Capacity: 90 Passengers, 4 Crew |
 DS Schaffhausen |     | DS Schaffhausen The Schaffhausen - a flush-deck vessel – was the last paddlesteamer operated by the Schweizer Dampfboot AG. Built: 1913 Top speed: 27 km/h Weight: 135 tons Power: 294 kW Capacity: 400 Passengers |
 MS Zürich |     | MS Zürich The more than 80 year old Zürich has its homeport in Romanshorn. It is still in use for public transportation on the Bodensee. Built: 1933 Top speed: 25 km/h Weight: 235 tons Power: 441 kW Capacity: 450 Passengers |
 Zoroaster |     | Zoroaster Many consider the Zoroaster to be the first successful oil tanker. Unlike later models, it was built small enough to sail canals and also the Volga River. Built: 1878 Top speed: 15 km/h Power: 210 kW Capacity: 240 Fluids |
 MGS Merlin |     | MGS Merlin The motor cargo vessel Merlin is a modern river cargo ship which travels on the Donau. Built: 1981 Top speed: 25 km/h Power: 1030 kW Capacity: 1865 Bulk |
 DS Rigi |     | DS Rigi The parts of the Rigi were built in England and assembled in Luzern. Due to the lack of coal in Switzerland at the time, the Rigi was powered by wood. Built: 1848 Top speed: 19 km/h Power: 24 kW Capacity: 200 Passengers |
 Hovercraft SR.N6 |     | Hovercraft SR.N6 The SR.N6 is a larger version of the SR.N5 series and became the most produced and successful hovercraft design in the world. Built: 1970 Top speed: 93 km/h Power: 780 kW Capacity: 58 Passengers |
 GD Wilhelm |     | GD Wilhelm The Wilhelm was built with the support of King Wilhelm I. of Württemberg and was officially the first steamer on the Bodensee. Built: 1824 Top speed: 10 km/h Power: 15 kW Capacity: 23 Bulk |
 GD Frontenac |     | GD Frontenac The Frontenac was built for 50.000 Dollars in New York and was in service on Cayuga Lake for several decades. Built: 1870 Top speed: 26 km/h Power: 37 kW Capacity: 350 Passengers |
 GMS Axalp |     | GMS Axalp The Axalp was designed by the famous Swiss naval architect Adolf J. Rynike. After commissioning it was upgraded several times. Built: 1949 Power: 662 kW Capacity: 1200 Bulk |
 MS Graf Zeppelin |     | MS Graf Zeppelin The Graf Zeppelin parts where build in Linz and finally put together in Fussach. Built: 1980 Top speed: 25 km/h Power: 678 kW Capacity: 700 Passengers |
 SS Klondike |     | SS Klondike The Klondike had the distinction of a much higher capacity then regular sternwheelers, despite its shallow draft. Built: 1921 Power: 391 kW Capacity: 270 Bulk |
 TMS Vandal |     | TMS Vandal The Vandal is one of the first ships build with a Diesel engines and an electrical transmission. Built: 1903 Top speed: 15 km/h Power: 265 kW Capacity: 800 Fluids |
 TMS Viola |     | TMS Viola The Violoa was built in Temse and was used to haul fuel on the Rhine river. Built: 1949 Power: 662 kW Capacity: 1200 Fluids |
Vehicle features have been discussed in detail in the development blog #1:
